Securing a home loan is a significant financial commitment, and understanding the implications of the interest per month is crucial for effective financial planning. Whether you are considering buying your dream home or investing in real estate, comprehending how the interest on a ₹20 lakh loan influences your monthly obligations is essential. This guide will walk you through the calculations, factors affecting interest rates, and tips for managing your loan effectively.
Let’s delve into each of these sections to give you a comprehensive understanding of how a ₹20 lakh home loan’s interest per month works.
What is Home Loan Interest?
Home loan interest is the cost you pay to a lender for borrowing money to purchase or construct a home. This interest is typically expressed as a percentage of the loan amount and is charged on a monthly basis. The rate at which this interest is charged is called the interest rate.
Types of Interest Rates
- Fixed Interest Rate: The interest rate remains constant throughout the loan tenure. This offers predictability in EMI payments.
- Floating Interest Rate: The interest rate varies based on market conditions, usually linked to a benchmark rate such as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) policy rates. This can lead to fluctuations in EMI amounts.
Components of Home Loan EMI
EMI (Equated Monthly Installment) consists of two parts:
- Principal Repayment: The portion of the EMI that goes towards repaying the original loan amount.
- Interest Payment: The portion of the EMI that goes towards paying the interest on the outstanding loan amount.
EMI Calculation Formula
The formula for calculating EMI is:
![]()
Where:
- P = Principal loan amount
- R = Monthly interest rate (annual rate divided by 12 and then divided by 100)
- N = Number of monthly installments
Calculating Interest Per Month
To understand how much interest you pay per month, you need to break down your EMI into its interest and principal components. Initially, the interest component is higher, and over time, the principal repayment increases.
Example Calculation
Assume you have a ₹20 lakh loan at an 8.45% annual interest rate for 20 years.
- Monthly Interest Rate (R):
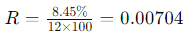
- EMI Calculation:
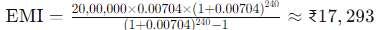
- Monthly Interest for the First Month:
Interest = Principal × Monthly Interest Rate
Interest = 20,00,000 × 0.00704 = ₹14,080
In the first month, out of ₹17,293 EMI, ₹14,080 goes towards interest, and the remaining ₹3,213 goes towards principal repayment.
Factors Influencing Interest Rates
Several factors can influence the interest rate you are offered on a home loan:
Credit Score
A higher credit score can lead to lower interest rates as it reflects your creditworthiness.
Loan Tenure
Longer tenures might attract higher interest rates but result in lower monthly EMIs. Shorter tenures can have lower interest rates but higher EMIs.
Loan Amount
Larger loans might come with lower interest rates due to the economies of scale.
Type of Employment
Salaried individuals might get better rates compared to self-employed individuals due to perceived stability.
Economic Conditions
Market conditions and RBI policies influence the base rates, affecting the home loan interest rates.
Different Interest Rate Types
Understanding the difference between fixed and floating rates is essential for choosing the right loan:
Fixed Interest Rate
- Pros: Predictability, stable EMIs.
- Cons: Might be higher initially, no benefit from falling interest rates.
Floating Interest Rate
- Pros: Potential to benefit from falling rates.
- Cons: EMI fluctuations, harder to predict long-term costs.
Amortization Schedule
An amortization schedule provides a breakdown of each EMI into principal and interest components over the loan tenure. It shows how the interest component decreases while the principal component increases over time.
Example Amortization Schedule for First Year
| Month | EMI | Interest | Principal | Outstanding Principal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17,293 | 14,080 | 3,213 | 19,96,787 |
| 2 | 17,293 | 14,038 | 3,255 | 19,93,532 |
| … | … | … | … | … |
| 12 | 17,293 | 13,446 | 3,847 | 19,54,226 |
Impact of Loan Tenure on Monthly Interest
The loan tenure significantly impacts the EMI and the total interest paid over the loan period:
Shorter Tenure
- Higher EMIs
- Lower Total Interest
Longer Tenure
- Lower EMIs
- Higher Total Interest
Strategies to Minimize Interest Payments
To reduce the interest burden, consider the following strategies:
Higher Down Payment
Increase your down payment to reduce the principal amount and thereby the interest.
Prepayment
Make lump-sum payments towards the principal when possible.
Shorter Tenure
Opt for a shorter loan tenure to reduce total interest outgo.
Importance of Prepayment and Part-Payment
Prepayment and part-payment can help in reducing the overall interest burden:
Full Prepayment
Clears the outstanding loan amount, leading to substantial interest savings.
Part-Payment
Reduces the principal, leading to lower interest in future EMIs.
Using an EMI Calculator
An EMI calculator is a tool that helps you calculate your monthly EMI based on the loan amount, interest rate, and tenure. It simplifies complex calculations and provides quick results.
Steps to Use an EMI Calculator
- Enter Loan Amount: ₹20,00,000
- Enter Interest Rate: 8.45%
- Enter Loan Tenure: 20 years
The calculator provides the EMI, total interest payable, and the total payment amount.
Comparing Different Interest Rates and Offers
It’s crucial to compare different lenders’ interest rates and offers before finalizing a home loan. Look for:
- Lower interest rates
- Special offers or discounts
- Flexible repayment options
- No hidden charges
Impact of Credit Score on Interest Rates
A higher credit score (750+) can help you secure a lower interest rate, reducing your EMI and total interest payout.
Improving Your Credit Score
- Timely Payments: Pay existing loans and credit card bills on time.
- Credit Utilization: Keep credit card utilization low.
- Credit Mix: Maintain a healthy mix of secured and unsecured credit.
Government Schemes and Benefits
Various government schemes can provide subsidies and benefits on home loans:
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY)
Offers interest subsidies to first-time homebuyers in specific income groups.
Subsidies for Women Borrowers
Some schemes offer reduced interest rates for female borrowers.
Document Requirements and Loan Application Process
Documents Required
- Identity Proof: PAN, Aadhaar
- Address Proof: Utility bills, passport
- Income Proof: Salary slips, bank statements
- Property Documents: Sale agreement, property tax receipt
Application Process
- Download App or Visit Bank: Fill out the application form.
- Submit Documents: Provide necessary documents.
- Loan Sanction: Bank verifies documents and processes the loan.
- Disbursement: Loan amount is credited to your account.
Monthly Interest Rates by Bank
In India, various banks offer different interest rates on loans. Below is a list of prominent banks with indicative interest rates for a ₹20 lakh loan:
| Bank Name | Home Loan Interest Rate | Personal Loan Interest Rate | Car Loan Interest Rate | Education Loan Interest Rate | Business Loan Interest Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State Bank of India (SBI) | 6.75% – 9.0% | 10.5% – 13.5% | 8.0% – 12.0% | 8.5% – 11.5% | 11.5% – 16.0% |
| HDFC Bank | 6.75% – 8.5% | 11.0% – 14.5% | 8.5% – 13.5% | 9.0% – 12.5% | 12.5% – 18.0% |
| ICICI Bank | 7.0% – 9.5% | 10.99% – 15.5% | 9.0% – 14.0% | 9.5% – 13.0% | 13.0% – 19.0% |
| Axis Bank | 6.9% – 8.8% | 12.0% – 15.75% | 8.9% – 13.5% | 9.25% – 12.75% | 12.75% – 18.5% |
| Punjab National Bank (PNB) | 6.8% – 8.9% | 11.5% – 14.0% | 8.25% – 12.75% | 8.75% – 11.75% | 11.75% – 17.0% |
| Bank of Baroda | 6.75% – 9.2% | 11.5% – 14.75% | 8.75% – 12.85% | 8.75% – 12.0% | 12.0% – 17.5% |
| Kotak Mahindra Bank | 6.6% – 8.75% | 11.5% – 16.0% | 8.5% – 14.0% | 9.5% – 13.0% | 13.0% – 18.5% |
| Canara Bank | 6.85% – 9.1% | 10.75% – 14.0% | 8.75% – 13.0% | 8.75% – 12.5% | 12.0% – 17.25% |
| Union Bank of India | 6.7% – 9.05% | 11.0% – 14.5% | 8.65% – 13.25% | 8.65% – 12.75% | 12.5% – 18.0% |
| IDFC FIRST Bank | 6.75% – 8.9% | 10.99% – 15.75% | 8.9% – 14.5% | 9.0% – 12.5% | 12.5% – 19.0% |
| IndusInd Bank | 6.9% – 9.1% | 11.25% – 16.0% | 9.25% – 13.5% | 9.25% – 12.5% | 13.5% – 19.5% |
| Yes Bank | 6.75% – 9.0% | 11.0% – 15.5% | 8.75% – 14.0% | 9.0% – 12.75% | 12.5% – 18.5% |
| Federal Bank | 6.75% – 8.95% | 10.99% – 15.0% | 8.9% – 13.75% | 9.0% – 12.5% | 12.5% – 17.5% |
| Bank of India | 6.85% – 9.25% | 11.5% – 15.0% | 8.8% – 13.75% | 9.0% – 12.75% | 12.75% – 18.25% |
| Indian Bank | 6.8% – 9.1% | 11.0% – 14.5% | 8.65% – 13.5% | 8.75% – 12.5% | 12.5% – 18.0% |
| Central Bank of India | 6.75% – 9.0% | 11.25% – 14.25% | 8.5% – 13.5% | 8.75% – 12.5% | 12.0% – 17.5% |
| UCO Bank | 6.7% – 8.95% | 11.5% – 14.5% | 8.75% – 13.0% | 8.65% – 12.75% | 12.75% – 18.25% |
| Andhra Bank | 6.75% – 9.0% | 11.25% – 14.75% | 8.5% – 13.5% | 8.75% – 12.5% | 12.5% – 18.0% |
| Corporation Bank | 6.8% – 9.05% | 11.0% – 14.25% | 8.6% – 13.25% | 8.75% – 12.75% | 12.75% – 17.75% |
| Bank of Maharashtra | 6.85% – 9.1% | 11.0% – 14.75% | 8.75% – 13.0% | 8.75% – 12.5% | 12.5% – 18.0% |
| Karnataka Bank | 6.8% – 8.95% | 10.99% – 15.5% | 8.9% – 14.0% | 8.9% – 12.75% | 12.75% – 18.5% |
| South Indian Bank | 6.9% – 9.2% | 11.25% – 15.75% | 8.95% – 13.75% | 9.0% – 12.75% | 12.75% – 18.0% |
| Saraswat Bank | 6.75% – 9.05% | 11.5% – 15.25% | 8.75% – 13.5% | 9.0% – 12.5% | 12.75% – 18.5% |
| RBL Bank | 6.75% – 8.9% | 11.0% – 15.5% | 8.75% – 13.75% | 9.0% – 12.5% | 12.75% – 18.25% |
| Bandhan Bank | 6.7% – 8.85% | 11.25% – 15.75% | 8.75% – 13.5% | 9.0% – 12.5% | 12.75% – 18.25% |
| L&T Finance | 6.8% – 9.2% | 11.5% – 16.0% | 9.0% – 13.5% | 9.25% – 12.75% | 13.0% – 18.75% |
| Bajaj Finserv | 6.75% – 9.1% | 11.5% – 16.5% | 9.0% – 14.0% | 9.0% – 12.75% | 12.75% – 18.5% |
| Tata Capital | 6.85% – 9.3% | 11.5% – 16.25% | 9.25% – 13.75% | 9.0% – 12.75% | 13.0% – 18.75% |
| Mahindra Finance | 6.9% – 9.2% | 11.75% – 16.5% | 9.5% – 14.0% | 9.5% – 13.0% | 13.25% – 19.0% |
| Muthoot Finance | 7.0% – 9.5% | 12.0% – 16.75% | 9.5% – 14.5% | 9.75% – 13.0% | 13.5% – 19.5% |
Tax Benefits on Home Loan Interest
Section 24(b)
Allows deduction of up to ₹2 lakh per annum on interest paid for a self-occupied property.
Section 80EE
Provides an additional deduction of up to ₹50,000 for first-time homebuyers.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Ignoring the Total Cost
Don’t just focus on EMI; consider the total cost including interest.
Not Comparing Offers
Always compare different lenders’ offers.
Overlooking Prepayment Charges
Check for prepayment or foreclosure charges before finalizing a loan.
Conclusion
Understanding the interest per month on a ₹20 lakh home loan is crucial for managing your finances effectively. By comprehending how EMIs are structured, factors affecting interest rates, and strategies for minimizing interest payments, you can make informed decisions and reduce your overall loan burden. Use the insights and tools provided in this guide to plan your home loan efficiently and achieve your homeownership goals with confidence.
FAQs about ₹20 Lakh Home Loan Interest Per Month
Can I switch from a floating to a fixed interest rate?
Yes, many lenders allow you to switch but it might involve a conversion fee.
What happens if I miss an EMI payment?
Missing an EMI can lead to penalties and affect your credit score. Repeated defaults can lead to legal action.
Can I negotiate the interest rate?
Yes, with a good credit score and financial stability, you can negotiate for a better rate.
How does the repo rate affect home loan interest rates?
Repo rate changes by the RBI can lead to changes in floating interest rates as lenders adjust their rates accordingly.
What is the difference between reducing balance and flat rate interest?
- Reducing Balance: Interest is calculated on the outstanding principal, leading to lower interest over time.
- Flat Rate: Interest is calculated on the entire principal for the entire tenure, leading to higher interest.
How is the monthly interest calculated for the first year of my home loan?
Monthly interest is calculated based on the outstanding principal at the beginning of each month. For instance, with a ₹20 lakh loan at 8.45% annual interest, the first month’s interest would be:
![]()
What is the difference between EMI and SIP?
- EMI (Equated Monthly Installment): Fixed monthly payment that includes both principal and interest, used for loan repayment.
- SIP (Systematic Investment Plan): Regular investment of a fixed amount into mutual funds, not related to loans.
Can the interest rate change during the tenure of my loan?
Yes, if you opt for a floating interest rate, it can change based on market conditions or changes in the lender’s benchmark rates. A fixed interest rate remains constant throughout the loan tenure.
How does a balance transfer affect my home loan interest?
A home loan balance transfer involves transferring your existing loan to another lender offering a lower interest rate. This can reduce your EMI or total interest outgo but might involve processing fees or other charges.
What happens if I fail to pay my EMI on time?
Late EMI payments can result in:
- Late Payment Fees: Additional charges for missing the due date.
- Negative Impact on Credit Score: Can affect your creditworthiness.
- Legal Action: Repeated defaults can lead to foreclosure or other legal consequences.
How can I calculate the total interest paid over the loan tenure?
To calculate the total interest paid, multiply the EMI by the total number of installments and subtract the principal amount from the result:
Total Interest Paid = (EMI × Total Number of Installments) − Principal Amount
Can I change my loan tenure midway?
Yes, many lenders allow you to restructure your loan, which might involve extending or reducing the tenure based on your current financial situation. This can impact your EMI and total interest.
Are there any tax benefits on prepayment of a home loan?
Prepayments reduce the principal amount, which can lower your interest outgo and result in tax benefits under Sections 80C and 24(b) for the principal and interest components, respectively.
Is it better to invest or prepay the home loan?
This depends on the returns from investments versus the interest rate on the loan. If investment returns exceed the loan interest rate, investing might be preferable. Otherwise, prepaying the loan can save on interest costs.
How does foreclosure impact my credit score?
Foreclosure, or full repayment of the loan before its tenure, generally does not negatively impact your credit score. In fact, it can improve your score by demonstrating your ability to manage and repay debt.
What is the processing fee, and how does it affect my home loan?
The processing fee is a one-time charge by the lender for processing your loan application. It typically ranges from 0.5% to 1% of the loan amount and adds to the overall cost of the loan but does not affect monthly interest directly.
How can I avail of a home loan interest subsidy?
Government schemes like Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) offer interest subsidies based on income criteria and other eligibility factors. You need to apply through the bank or lender offering this subsidy and provide the required documentation.
Can I refinance my home loan with another lender to get a better rate?
Yes, refinancing or balance transfer allows you to switch to another lender offering a lower interest rate. It can reduce your EMI or total interest but may involve fees for the transfer.
What is the impact of part-payment on my loan interest?
Part-payment reduces the outstanding principal, which in turn reduces the interest component of future EMIs. This can shorten the loan tenure or reduce the EMI amount, depending on the lender’s policy.
How does inflation affect home loan interest rates?
Inflation can lead to changes in monetary policy by central banks, influencing interest rates. High inflation might lead to increased interest rates, while low inflation could lead to lower rates.
What is the significance of the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio in determining interest rates?
The LTV ratio is the loan amount as a percentage of the property value. A lower LTV ratio (i.e., higher down payment) often attracts lower interest rates because it reduces the lender’s risk.
Can I negotiate the processing fee with my lender?
Yes, processing fees can sometimes be negotiated, especially if you have a strong credit profile or are transferring a large loan amount. Some lenders might also offer discounts or waivers during promotional periods.
How often can I change my EMI payment date?
Changing the EMI payment date typically depends on the lender’s policies. Some lenders allow flexibility to adjust the date based on your salary credit date or other financial considerations.
What is an EMI holiday, and how does it affect my interest?
An EMI holiday allows borrowers to defer payments for a specific period, often offered during festivals or to new borrowers. Interest continues to accrue during this period, increasing the total payable amount later.
How do joint home loans affect interest rates and EMIs?
In a joint home loan, two or more people share the responsibility for repayment. This can lead to eligibility for a higher loan amount and potentially better interest rates if all co-applicants have strong credit profiles. However, all co-applicants are equally responsible for repayment.
How do fluctuations in the repo rate impact my floating interest home loan?
Changes in the repo rate (the rate at which RBI lends to commercial banks) directly affect floating interest rates. A reduction in the repo rate usually leads to lower floating rates and vice versa.
What are the implications of linking my loan to the MCLR?
The MCLR (Marginal Cost of Funds-based Lending Rate) is the benchmark lending rate for banks. Loans linked to MCLR are subject to periodic rate reviews, which can result in changes in your EMI based on the latest MCLR adjustments.
Can a higher initial down payment reduce my interest rate?
Yes, a higher down payment can reduce the principal amount you need to borrow, potentially qualifying you for lower interest rates as it reduces the lender’s risk.
What is a step-up home loan, and how does it affect interest payments?
A step-up home loan allows for lower EMIs in the initial years, which gradually increase. This can be beneficial if you expect your income to rise over time. Interest accrues as per the increased EMIs, making it easier to manage initially but potentially increasing the total interest cost.
How do lenders assess the value of my property for loan purposes?
Lenders typically assess the property value through their appointed valuers, who consider factors like market value, location, and construction quality. This value impacts the loan amount you can borrow, influencing the LTV ratio.
What role does the base rate play in determining my home loan interest rate?
The base rate is the minimum interest rate set by banks below which they cannot lend, except for special cases. Your loan’s interest rate is often set above this base rate, and any changes in the base rate can affect your loan’s floating interest rate.
How does a green home loan differ in terms of interest rates?
Green home loans are designed for properties meeting certain energy efficiency or environmental standards. These loans may offer lower interest rates or additional incentives to promote sustainable living.
What is the impact of economic downturns on home loan interest rates?
During economic downturns, central banks might lower interest rates to stimulate the economy. This can lead to reduced home loan interest rates, lowering your EMI if you have a floating rate loan.
How does the RBI’s policy impact home loan interest rates?
The RBI’s monetary policies, such as changes in the repo rate or cash reserve ratio, directly impact banks’ lending rates. An increase in the repo rate usually leads to higher interest rates for borrowers, and a decrease leads to lower rates.
What happens if I sell my property before fully repaying the loan?
If you sell your property before the loan is repaid, the outstanding loan amount must be cleared from the sale proceeds. The bank will typically issue a No Objection Certificate (NOC) once the loan is settled.
Can I opt for a moratorium on home loan interest payments during a financial crisis?
During crises like the COVID-19 pandemic, RBI allowed moratoriums where borrowers could defer EMI payments. Interest continued to accrue during the moratorium, increasing the overall repayment amount later.
How does the interest subsidy scheme work for affordable housing loans?
Under schemes like PMAY, eligible borrowers receive a subsidy on interest rates for loans on affordable housing. The subsidy is credited to the loan account, reducing the principal and thereby lowering EMIs.
How are interest rates different for NRI home loans compared to resident home loans?
Interest rates for NRI home loans can be slightly higher than those for resident home loans due to perceived higher risk. Additionally, NRI loans might have stricter documentation and eligibility criteria.
Can I switch my home loan from a fixed to a floating rate?
Yes, many lenders allow switching from a fixed to a floating rate during the loan tenure. This might involve paying a conversion fee and is usually subject to the lender’s terms and conditions.
What is the process for claiming tax deductions on home loan interest?
To claim tax deductions under Sections 24(b) and 80EE:
- Section 24(b): Show the interest paid certificate from your lender while filing your tax returns.
- Section 80EE: Ensure you meet the eligibility criteria (first-time homebuyer, loan amount not exceeding ₹35 lakh, property value not exceeding ₹50 lakh).


1 Comment